Model Selection
Model Complexity
What is model complexity? Perhaps it mainly refers to the number of parameters that the model has. However, it does not mean that a model is complex if it has more parameters, although it is often the case. Generally, a simple model could result in underfitting, while a complex model could lead to overfitting. So, what factors affect the complexity of a model? Well, it is hard to say. Often,
- a model with more parameters
- a model whose parameters take a wider range of values
- a model that takes more training iterations
Model Selection
In machine learning, we care about two factors that affect model performance
- model
- training data
The process of selecting the best model is known as model selection. In practice, it includes two parts
- select the best model from a list of candicate models
- search the best parameters for the best model
Validation Dataset
To select the best model, we need another dataset to validate our hypothesis, which is the validation dataset. Why? Training data are used for training models, and test data are used to measure the performance of generalisation, which can only be used once. If we use test data to do model selection and then test the generalizability of the best model, we face data leakage since the selected model has already seen test data. Thus, we need to hold out a new dataset for validation only. In practice, data will be split into 70% for training, 10% for validation, and 20% for testing.
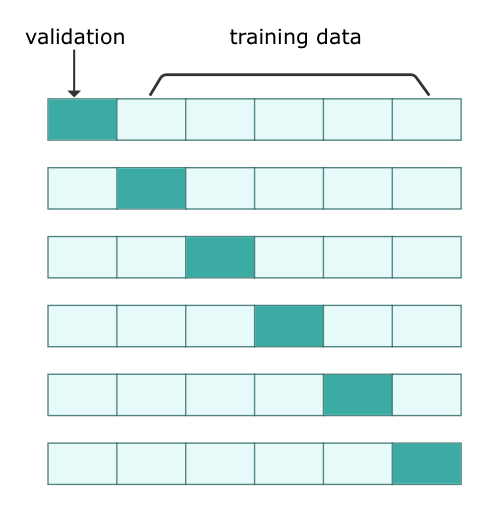
K-Fold Cross-validation
But what if we have scarce data? Taking out some data for validation and testing will further result in fewer training data. To tackle this, we employ cross-validation to resample data. Specifically, we split data into several equal-sized groups, and leave out one group as validation dataset once a time. That is, if there are $K$ groups, we will repeat $K$ times. Then, we take the average of the $K$ validation scores. In doing so, we can make the most of training data.